What is a dermatologist?
A dermatologist is a medical specialist in dermatology, a medical branch that focuses on diagnosing, treating, and preventing skin, hair, and nail conditions. Dermatologists are trained to address various skin issues, including common conditions like acne, eczema, rashes, and skin cancer, and cosmetic concerns like scars and wrinkles.
What do dermatologists do?
Dermatologists play a crucial role in outpatient clinics, managing acute and chronic skin diseases through interventions and patient education.
Investigation and Management: Dermatologists specialize in investigating, managing, and treating various skin conditions, hair problems, and nail issues.
Comprehensive Treatment: They go beyond diagnosis, providing comprehensive treatment plans for dermatological conditions ranging from common skin ailments to more complex ones.
Surgical Expertise: Dermatologists are skilled in performing surgical procedures related to the skin, including excisions, biopsies, and other interventions to promote skin health and aesthetics.
Collaboration with Specialists: They collaborate closely with other specialists, such as oncologists and plastic surgeons, to offer a holistic approach to managing complex cases.
Frontline Practitioners: In outpatient clinics, dermatologists serve as frontline practitioners, addressing acute and chronic skin diseases through interventions and patient education.
Patient Education: A crucial aspect of their role is empowering individuals to understand and actively participate in their skin health journey.
Guardians of Skin Health: Dermatologists are not just medical professionals; they are guardians of the body’s largest organ, working tirelessly to ensure the health, vibrancy, and aesthetics of the skin.
What training and qualifications do dermatologists have?
Becoming a dermatologist requires extensive education and training. The typical path includes:
- Obtaining a bachelor’s degree.
- Completing medical school (usually four years).
- A dermatology residency (another four years).
Dermatologists must also obtain a license and may choose to become board-certified through organizations like the American Board of Dermatology.
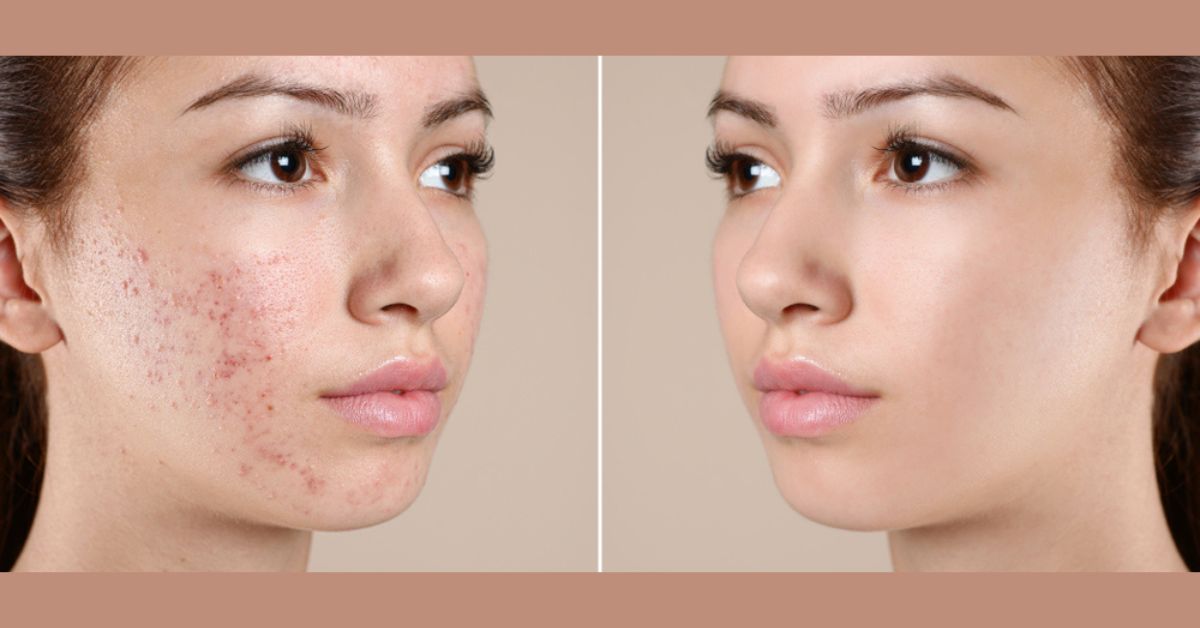
What are common conditions that dermatologists treat?
Dermatologists treat conditions like acne, eczema, rashes, skin cancer, and cosmetic concerns like scars and wrinkles. They also diagnose and manage issues related to hair, nails, and mucous membranes. Additionally, dermatologists may specialize further in areas like pediatric or cosmetic dermatology.
What types of procedures do dermatologists perform?
Dermatologists perform various methods, including surgical interventions for skin conditions like skin cancer or cosmetic procedures such as laser treatments for hair removal or skin tightening. They are skilled in diagnosing skin diseases through clinical examinations and may also engage in research or teaching activities.
What are some dermatology subspecialty fields?
Dermatology offers subspecialties such as cosmetic dermatology, dermatopathology, immunodermatology, Mohs surgery, and pediatric dermatology. Each subspecialty focuses on specific aspects of dermatological care, such as investigating the origin of skin diseases (dermatopathology) or treating children’s skin conditions (pediatric dermatology)
What is the difference between dermatologists and estheticians?
Dermatologists and estheticians play distinct roles in skincare, and their qualifications, scope of practice, and the nature of their work differ. Here are the critical differences between dermatologists and estheticians:
Dermatologists:
Medical Training: Dermatologists are medical doctors (MDs) or doctors of osteopathic medicine (DOs) who undergo extensive medical education and training.
Medical Conditions: They diagnose and treat various medical skin conditions, including skin cancer, infections, and autoimmune diseases.
Prescriptive Authority: Dermatologists can prescribe medications, including antibiotics and topical treatments, and perform medical procedures such as biopsies and surgeries.
Medical Procedures: They perform skin biopsies, excisions, laser treatments, and Mohs surgery for skin cancer.
Estheticians:
Cosmetic Training: Estheticians receive skincare and cosmetic treatment training but are not medical doctors.
Skincare and Beauty: They focus on improving the appearance of the skin, offering services such as facials, chemical peels, and microdermabrasion.
Limited Medical Conditions: Estheticians address cosmetic concerns like acne, aging, and pigmentation but do not diagnose or treat medical skin conditions.
No Prescriptive Authority: Estheticians cannot prescribe medications and do not perform medical procedures such as surgery or biopsies.
Relaxation and Wellness: Estheticians often work in spa settings, providing relaxing treatments that contribute to overall well-being.
When should I make an appointment with a dermatologist?
You should consider seeing a dermatologist if you have concerns about your skin health, such as persistent acne, unusual moles or growths, chronic rashes, or eczema that do not improve with over-the-counter treatments or signs of skin cancer. Regular skin check-ups are also recommended for early detection of potential issues.
How should I prepare for my first dermatologist appointment?
Before your first appointment with a dermatologist, it’s helpful to list your current skincare routine, any medications you are taking (including over-the-counter products), and previous skin conditions or treatments. Be prepared to discuss your concerns in detail during the appointment to help the dermatologist make an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.





One Response
Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.